|
|
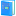
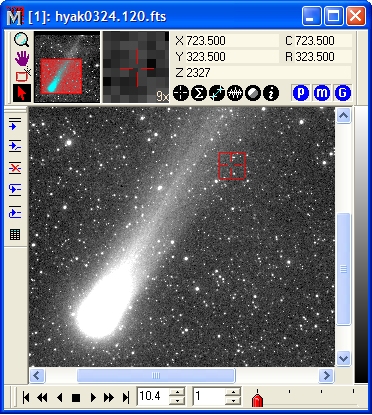
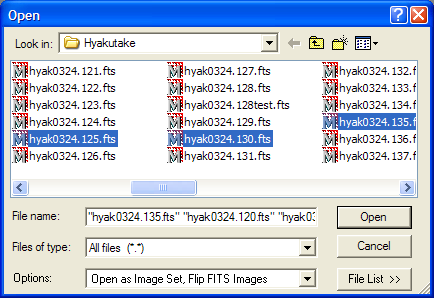
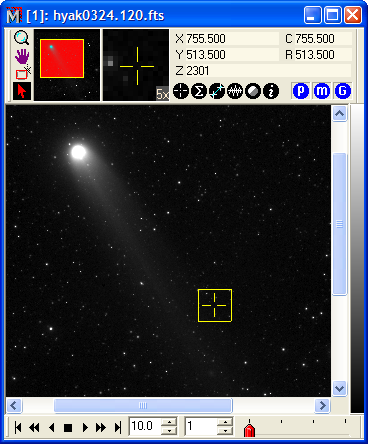
Tutorial: Displaying an Image Set This tutorial extends the concepts learned in Tutorial: Displaying an Image. Here you will learn how to open multiple images to work them as an Image Set, animate them like a movie, make some measurements, and save the files. Opening FilesClick File > Open... to show the familiar Open dialog shown below. Select the 4 images as shown below and click [Open]. Note: Marking these 4 files involves the standard Windows protocol to select multiple files by holding down the [Shift] key. To mark files that are not in a contiguous block, use the [Ctrl] and [Shift] keys in the normal way.
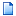
At the bottom of the dialog, notice that Open as Image Set option is enabled (drop the list box to see it as a check box option). This instructs Mira to load the selected images into the same Image Window. Multiple images constitute an Image Set, which is a Mira concept for working with multiple images as one object. If the Load As Image Set item is not checked, then the selected files are opened "traditionally" into different windows. Since an Image Set is chosen, the Image Window opens with an Animation Bar along its bottom border. This toolbar lets you select the active image (that is, the one on top) or to move between them. You can switch between images one at a time or by playing them as a movie using a chosen frame rate and step.
Changing the Image SetMira provides tools for adding, deleting, and reordering the image set. These are most conveniently accessed using the Image Set Toolbar, which can be quickly opened or closed using a keyboard accelerator or a menu command. Now, press the key combination Ctrl+Q to open the Image Set Toolbar. The toolbar opens attached to the left border of the current Image Window as shown below.
Using the toolbar is simple and some of its
commands work in conjunction with the
Image Animation Bar at the bottom of the Image
Window. For example, to insert one or more images into the image
set before the second image, move the selection trackbar on the
Animation Bar to position 2, then click One additional way to insert images into an image window is by using the Copy+ Paste commands in the Edit menu. The Copy command places a copy of the current visible image from any image window onto the Windows clipboard. This clipboard image can be pasted into any other image window to append the image set already there. Blinking and Animating ImagesOn the Animation Bar, click Using a File ListNow that we have opened an image set, let's see how we can easily work with this same image set in the future. Click File > Open to go back to the Open dialog. If we had any plans to use this same set of image in the future, here is what we should have done in the first place: Create a File List containing the target images. The File List contains the full path name of selected files. Mira works with a File List just a like a file, except that it knows that the File List contains the names of other files. In fact, a file list can contain other file lists, even mixed with individual image names. Let us create a File List containing 4 image files. First, open the standard Open dialog and click on the 4 images to open, like this (Use the standard Windows [Shift] and [Ctrl] key combinations to mark multiple files):
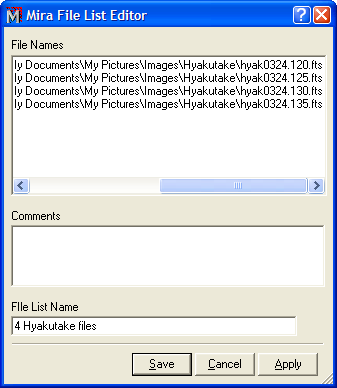
After marking the target images, click [File List >>] on the bottom of the dialog. This opens the File List Editor as shown below.
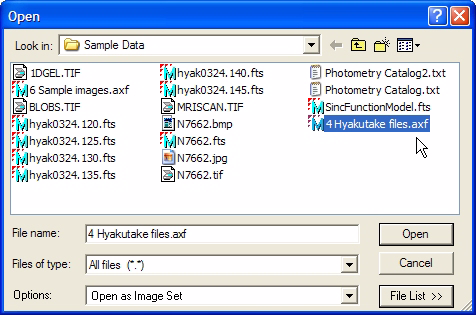
I the above figure the path names are scrolled to the right to show the file name on the right end. As you can see, the Comments and File List Name fields are initially blank. To create a File List, you must enter a name into the File List Name field and optionally, you can add some comments to the Comments field. When you are finished, click [OK] to save the new File List and return to the Open dialog. In the Open dialog, there is a new file with the name you gave to the File List. Here we have named it 4 Hyakutake files; when you click [OK], Mira creates a file named '4 Hyakutake files.axf'. After a short time, the new file name automatically appears in the Open dialog, as shown below. In the future, you will be able to open these same 4 images simply by selecting the File List by name. Let's try that now: Click on the new file list to select it as shown below.
Now, click the [Open] button. The next figure shows the result of opening the file list:
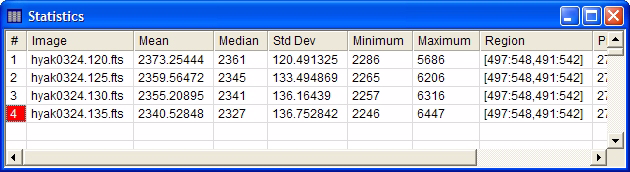
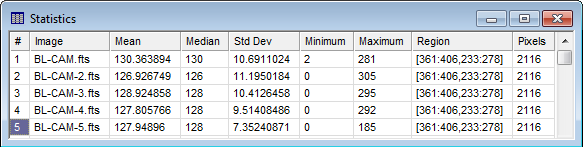
There are more things you can do with a File List, such as opening two of them into the same window. See Working with File Lists. Measuring Image StatisticsNow let us measure the statistics in the same
rectangular region of interest on the 4 images that we just loaded.
To do this, make sure the Image Window containing the 4 images has
the focus (in other words, it is on front of the stack). On the
Image Bar, there are two buttons to use. First, check that
Conversely, if the measure button is popped out,
like
Of course, the region being measured may be changed
by adjusting the
Image Cursor and then re-measuring. Additional
statistics measurements are written to this same window. You can
also measure only 1 image by popping out the Plotting a Row ProfileOne of the many types of plots Mira can display is
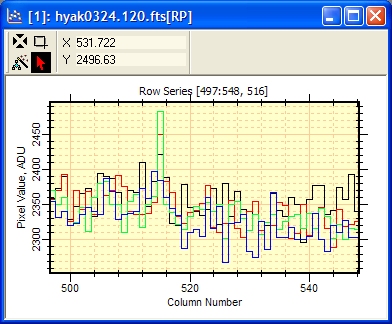
a Row Profile Plot, which shows the variation in image intensity
along a row. The Column Profile Plot shows the variation along a
column. For
Column Profile Plots and
Row Profile Plots, and for some other plots and
measurements, the region of interest is marked using the
Image Cursor. Before making the plot, we must answer
the following question: Do we want to plot the average row profile
for a single image or do we want to plot the same row profile for
the entire image set? The choice is made using the Image Set Plot button
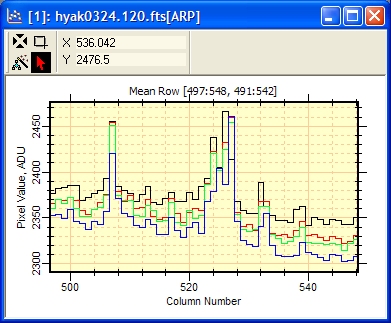
In the window above, each plot series uses a different color. You can choose these colors or set them all to the same color using the Plot Properties dialog. You can also animate the plot series much as you would the Image Set using the Plot Animation Bar. Notice that the window title has the suffix [RP], which means "Row Profile". Another interesting plot might be the
Average Row Profile, which plots the mathematical
average of all rows inside the Image Cursor. To choose the active
image or all images, we again set the
Saving ImagesFinally, lets suppose we performed some processing on the image set images and we will save the images back to files. We can save to the original files or to other files. The alternatives are described in Saving Image Sets. Here will will save the image set over the original files: Click File > Save Image Set > Save All. Using other commands in the Save Image Set submenu, we can save all images to a different folder, append a suffix to the file names, or create a new File List. Related Topics
Mira Pro x64 User's Guide, Copyright Ⓒ 2023 Mirametrics, Inc. All
Rights Reserved. |