|
|
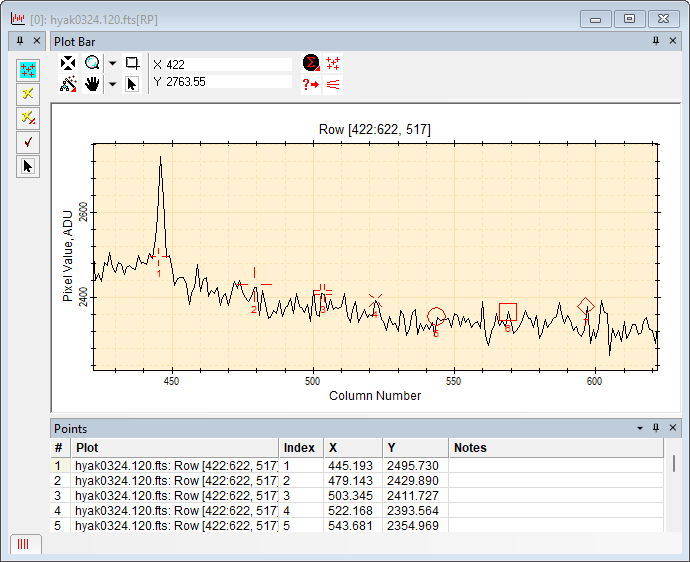
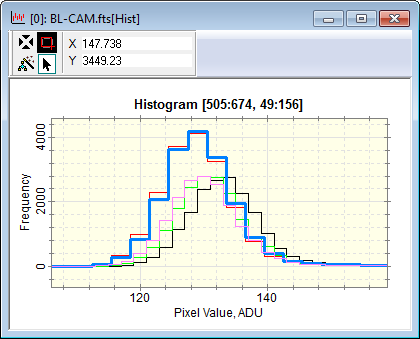
Plot Windows Plot Windows display 1-D data in the form of a 2-D graph, or "plot" and provide several tools for interactively working with the data. The different aspects of plotting data are described in Plotting Images and Data. The pictures below show a typical Plot Window with the Plot Bar at the top border and the Plot Animation Bar at bottom border. The Plot Bar can be shown or hidden using theToolbar command in the Plot menu or the option of the Image Plot Properties dialog. In the second picture, the window is changed to Overplot mode using the command in the Plot Context Menu. You can control whether Mira prompts you to confirm closing a Plot Window using the check list item in the General Properties dialog. Below is a typical Plot Window showing an image row plotted along with the Plot Bar at top, Plot Points Toolbar at the left, and the Points Measurements Pane at bottom. At the bottom left corner is the Plot Animation Bar reduced to a tab. An assortment of point markers is shown along the plot.
Since many plots are created from displayed images, Plot Windows can also link to the original source Image Window, Image, and pixel coordinates of the plot data in the image. See Go to Source Image. Script ExecutionThe Mira Pro Script language provides an immense collection of script functions and classes to work with Plot Windows and the Plot Series they contain. In addition, scripts can be executed (launched) directly from the Plot Window to work with its plot data. The Execute Script menu command opens for selecting a script, then executes the script. When the script is executed, it is automatically sent a CPlotView object and CPlot object attached to the window and the current plot series. Scripts can also be launched from grid measurement panes attached to the Plot Window. The installed folder <Documents>/Mira Pro x64 Data/Scripts/Samples contains a sample script to be called from the Plot Window, named "Execute from a Plot Window test.lua". See the Mira Pro x64 Script User's Guide for details. Displaying Multiple Plot SeriesA Plot Window can contain more than 1 series of data (that is, more than 1 plot), such as obtained from multiple images, multiple rows, or other sources. You can also create multiple plot series using copy + paste to add data from other Plot Windows. In such cases, you can choose from 2 modes to view the multiple series:
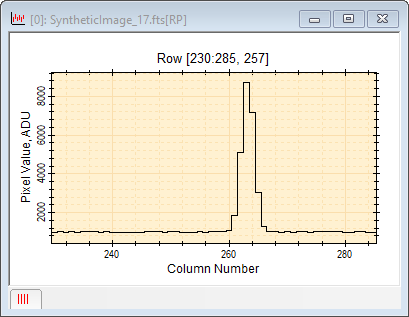
Animate ModeThis window has 5 plot series. In this mode, only 1 series is displayed at a time.
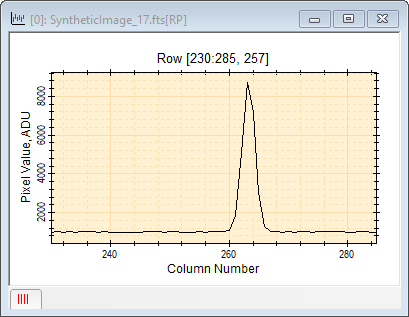
Overplot ModeThis picture shows all five plot series at the same time. The color assigned to each series is configured in the Plot Properties dialog. The Plot Series Properties also can be altered afterward using the Plot Series Properties dialog.
There are many ways to create Row Profile Plots and Column Profile Plots like those shown above. Plot Window ToolbarsThe Plot Window provides a number of toolbars for working with the plotted data.
Statistics MeasurementsUse the Measure > Statistics and Measure > Statistics Properties commands to compute statistics on the plot series data. These command are found in the Plot Window's pull-down menu and the Plot Bar. See the Statistics Measurements and Statistics Properties. A selected statistic can also be drawn in the Plot Window using the Mark Statistic command. Plot CoordinatesAll of the profile plots show image intensity versus position or distance. For these types, Mira also provides the following coordinate system options:
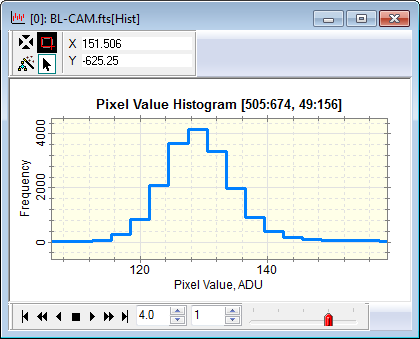
Intensity Profile PlotsIntensity is displayed on the vertical axis of a profile plot and the horizontal axis of a histogram plot. The Intensity Axis label includes the units of intensity if the image header contains such information. Default Line StyleLine graphs drawn in Plot Windows may default to either a stepped line or jagged line. The choice is made by setting the Default Line is Stepped Line option in the General Properties dialog (Ctrl+R). Below are shown the same plot made with the Default Line is Stepped Line option checked (left) and unchecked (right).
Changing the Plot PropertiesThe properties of the plot can be set before the plot is created and changed after the plot is created.
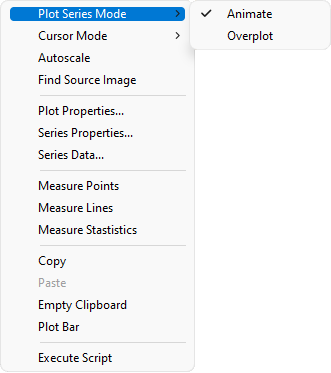
Plot Context MenuRight clicking inside a Plot Window opens a Context Menu containing several commands. These commands are duplicated in the pull-down menus but are collected here for quick access. The picture below shows the Plot Series Mode submenu opened and Animate mode selected for use by the Plot Animation Bar.
Shortcuts and Accelerator KeysThe Plot Window contains accelerator key shortcuts and single-key commands. The Plot Keys Pane describes all single keystroke commands for the Plot Window. Accelerator KeysAccelerators in the table below execute commands when a Plot Window has focus. Plot Accelerators
Saving Plot DataTo view the numeric plot data, user the Plot Series Data command. This opens the numeric data for all series into a grid window. The window has buttons to save, print, and copy the data to the Windows Clipboard. Use the Save as Text command to save the data to a file. This command is available from theFile menu when a Plot Window is the top-most view. Comparing Line Profile and Row Profile PlotsThe intensity profile of an image can be plotted using either the Column or Row Profile command or the Line Profile tool. There are some unique capabilities offered by each method. Comparison of Profile Plot Types
Plot CoordinatesAll of the profile plots show image intensity versus position or distance. For these types, Mira also provides the following coordinate system options:
Coordinate (Horizontal) Axis:
Intensity (Vertical) Axis: Intensity is displayed on the vertical axis of a profile plot and the horizontal axis of a histogram plot. The Intensity Axis label includes the units of intensity if the image header contains such information. Working with Plot SeriesA Plot Series is a series of points that create one plot. Multiple plot series can be considered to make a Plot Set, akin to the concept of an Image Set for Image Windows. As an example, consider a Column Profile plot which plots image intensity versus position along a single column with varying row number. If 5 such plots ("plot series") are created and shown in the same plot window, then the Plot Window contains a plot set of 5 plot series, with each series member being an individual plot. Why use the term "Plot Series" rather than just "Plot"? The reason for this extends from the fact that some Mira functions show a connected line plot for one data set in multiple segments. Each segment can be considered a plot of those data, but the multiple plots comprise only one plot series. When multiple plot series are displayed in the same Plot Window, they may be visualized in the following ways:
Averaging Adjacent LinesAdjacent lines (columns or rows) may be combined to form a single line to be plotted. The method of combining is controlled by the Plot Averaging Mode command. The name of the plot appears in the command menu from which the plot is created (see Plotting an Averaged Line). Plot Properties
Understanding the Plot Title and Plot CaptionsWindow TitleThe Plot Window title lists the image name from which the plot was created and gives an abbreviation that describes the type of plot. The plot type is abbreviated and appended to the window caption in square brackets. For example, a Row Plot is signified by [RP] appended to the Plot window caption. These suffixes appear in the window list of the Window menu and in the Multi-tab Interface along the bottom border of Mira's main window.
Plot CaptionThe Plot Caption is the text above the plot box but below the top window border. The Plot Caption tells you information about what was plotted. In particular, it may list the beginning and ending coordinates in (x,y) form for a Line Profile Plot or it may list the column and row range for a Column Profile or Row Profile plot. Below are some examples that show how to read the column,row range in the plot caption: Example Regions Listed in the Plot Caption
You can change the plot title, caption, and axis labels using the Labels page of the Plot Properties dialog. Related Topics
Mira Pro x64 User's Guide, Copyright Ⓒ 2023 Mirametrics, Inc. All
Rights Reserved. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||