|
|
Magnitude Calculations This topic describes how the Aperture Photometry package calculates the magnitudes and their random errors (or "uncertainties"). These quantities, as related to the table of photometry results, are also described in the topics Photometric Measurement Definitions and Photometric Error Definitions. This topic describes the math behind the calculations and how apertures are measured on an image. Calculating the MagnitudeMira computes the magnitude as m = K – 2.5 log ( Flux ) where
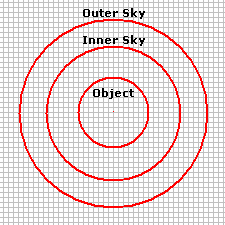
The camera gain ("Gain") and exposure time ("Exptime") are obtained from the FITS keywords GAIN and EXPTIME. The value of Counts is the net signal from the object, above the sky background, and measured in the raw pixel value units (often called "ADU's"). The Flux therefore represents a total number of electrons per second attributable to the object, above the sky. To compute the Flux, the image signal is summed over all pixels inside the innermost aperture, including the partially filled pixels along the rim of the aperture (see below). From this sum is subtracted the estimated sky brightness which is computed from pixels in the sky annulus formed between the 2 outer apertures. If the GAIN and EXPTIME keywords are not present in the image header, or they are wrong, you can add them or edit them using the Image Information page of the Aperture Photometry Properties dialog. Also see the topic Fixing Header Problems in Photometric Data. You can also change the names used for fetching the GAIN, EXPTIME, and RDNOISE values using the Photometry Keywords dialog. The value K is the photometric zero point. The zero point is assumed to be 0 or the value of the ZERO-PT keyword in the image header. If the value is 0, then the magnitude may be called a "raw magnitude". If a zero point value is computed for a particular instrumental setup and used in the calculation, the result is called "instrumental magnitude". If the zero point value, K, is unknown, it may be calculated using standard stars of known magnitude. Magnitude ErrorsThe uncertainty of the magnitude measurement is calculated in two ways: an empirical error, listed in the Report Window as Error, and a theoretical value listed as Error(T). The reported values may or may not include the uncertainty in the photometric zero point, which is calculated when more than 1 standard star is used. This option is controlled by the Include Zero Point Error check box on the Other Properties page. If checked, the reported error is the Root Sum Square ("RSS") value of the internal error of the measurement and the error of the mean of the zero point. The latter value is reported in the Photometry Results window. The empirical error involves the noise measured in the sky annulus as well as the values of GAIN, RDNOISE, and EXPTIME from the image header. The theoretical error uses the keywords but not the measured sky noise. The theoretical error estimate is the minimum possible uncertainty that could be measured at a given magnitude. You can change the values of GAIN, EXPTIME, and RDNOISE on the Image Information page. Doing so will change the error values by a small amount. Description of the AperturesThe aperture photometry procedure uses 3 apertures to measure an object:
The inner, object measuring aperture can be adjusted to any radius but, generally, it should not extend all the way to the point where the star appears to merge into the sky noise. Use the following guidelines to size the object aperture:
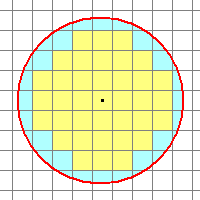
Regarding item 1, the object aperture can cut onto the star profile so long as it does the same for all star profiles. You can be totally safe by making the object aperture large enough to contain "all the light", but this adds more sky noise, which lowers the precision of the measurement and makes the magnitude errors larger. On the other hand, if the star profile varies over the region being measured, you might use an object aperture large enough to hold all the light for bright objects, or as the only option for measuring the field of view. The aperture photometry procedure uses 3 apertures to measure the object. The central aperture measures the total signal for the object while the local background is measure in the annulus between the outer two apertures. The apertures may be circular or elliptical, with any ellipticity and angle of rotation, but all three apertures have the same shape and are concentric. Elliptical apertures are used to measure objects when the Point Spread Function ("PSF") is elongated by poor tracking or other reasons. Matching the ellipse to the PSF shape gives a better measurement by maximizing the signal through the aperture of a given area, which in turn maximizes the signal to noise ratio. Small AperturesThe general placement of a measuring aperture on the pixel grid is shown below. In general, the object aperture, whether elliptical or circular, or at whatever angle, will have partially sampled pixels along its rim. For small apertures, a good measurement depends upon correctly accounting for the partial pixel coverage. Mira properly accounts for this case using a mathematically complex, but exact partial pixel algorithm—the only one of its kind.
The Ellipticity parameter is defined in terms of the axis ratio of the ellipse: for semimajor axis a and semiminor axis b, the Ellipticity is E = 1 - b/a. A circle has an ellipticity of 0. The major axis orientation and the "size" are adjustable using the Aperture Tool window. The size of an aperture is set as the "radius" defined as follows: Radius = square root( semimajor axis * semiminor axis ) = square root ( a * b ). All 3 apertures use the same Properties for every measurement. If measuring an image set, the Properties are the same for all images. Related TopicsPhotometric Measurement Definitions
Mira Pro x64 User's Guide, Copyright Ⓒ 2023 Mirametrics, Inc. All
Rights Reserved. |