|
|
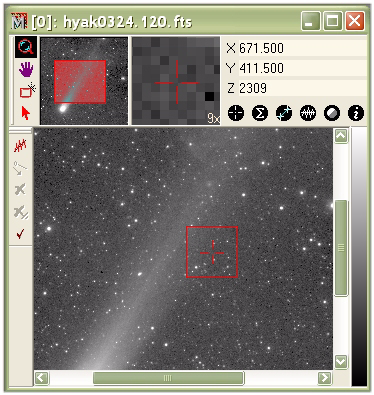
Tutorial: Creating Plots from Images This tutorial teaches you how to create intensity plots from images. In this exercise we will make Line Profile Plots and Row Profile Plots from one of the sample images. Also see Plotting Commands, Plotting Examples, Plot Windows, Chart Windows, and Examples of Row Plots. Open an ImageTo create a plot, we need to first display an image (see Tutorial: Displaying an Image). After starting Mira , click the File > Open command in the main menu bar. This opens the normal the Open dialog. In this dialog, navigate to the sample images in the folder "<Documents>\Mira Pro x64\Sample Data". Open the image named 'hyak0324.120.fts'. The displayed image will look like the one shown below. Note that the image may appear larger or smaller than shown here, depending upon how Mira scales it to fit the screen.
Now magnify and re-center the image so that it looks like the figure below. Next, open the Line Profile Toolbar by clicking on the main Image Plot Toolbar. The Line Profile Toolbar opens on the left side of the Image Window as shown below.
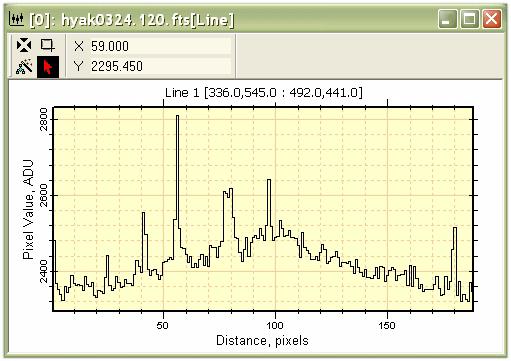
Plotting an Intensity ProfileA Line Profile Plot shows the change in intensity along a line drawn on the image. This type of plot uses the Line Profile Toolbar shown on the left side of the Image Window in the figure above. This is a standard Command Toolbar which was opened by clicking on the main Image Plot Toolbar at the top of the Mira application window. This toolbar opened in the typical mode with the top button (the marking mode) enabled. Using these toolbar buttons you can plot the intensity along any vector drawn on the plot and, as with other Mira plots, it works for both RGB images and non RGB images. To make a plot, mouse simply down at the starting point, then drag the line to its ending point and release the mouse. You will get a plot that looks like this:
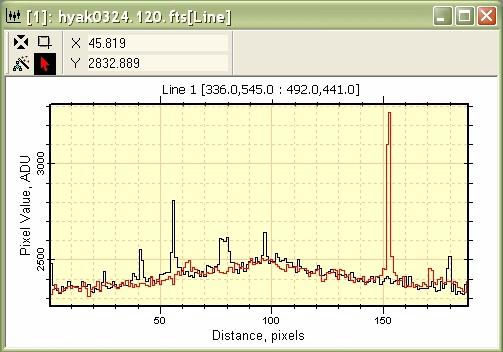
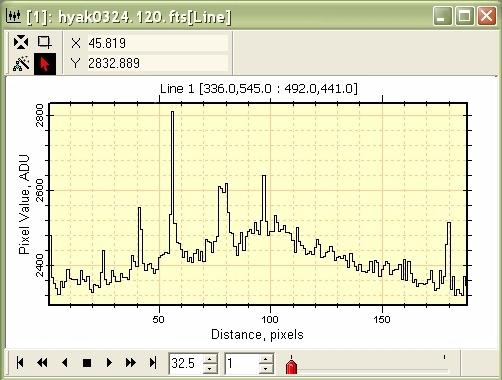
Next we want to know what is happening to pixels along a parallel line beside the one we just drew on the image. Click the second button on the toolbar to enter Move Mode for the marker (the line). Next, point at the line and click the mouse down to grab it and then drag the line to a new location as described in Move perpendicular. When the mouse is released, the next profile Over-plots the first one, like so:
We can continue adding plot series forever. But at
some point we will want to change to another mode, or click
Over-plotting and Animating PlotsWhen more than 1 plot series exists, you can choose to Overplot or animate them 1 series at a time. Right click on the plot to open the Plot Context Menu and select Plot Series Mode > Animate (you can also get this command from the Plot menu when an Image window has the focus) This command changes the window appearance to:
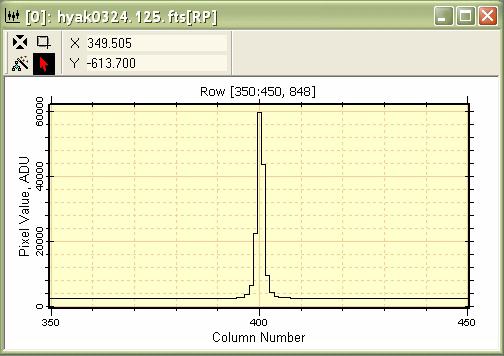
The Plot Animation Bar allows you to step or animate through the stack. Notice that you now see only 1 series at a time in Animate mode. You can switch back to Overplot in the same way. Using Overplot and Animate modes in a Plot Window is a parallel to what can be done in an Image Window using Mira's unique concepts of Image Sets and File Lists; these are covered in another tutorial. Plotting a Row ProfileNext, let us plot the profile of a single row through the peak of a star. To make a Column Profile Plot or Row Profile Plot, we use the Image Cursor to mark the extent of the plot. To plot a Row Profile, you must first adjust the Image Cursor to enclose the columns and rows you want to use. Often we would do that by moving and sizing the Image Cursor. In this case we may want to set the length of the plot (the number of columns) and we want to position it on the peak of a star. There are several ways to position the Image Cursor on the peak:
Now that the Image cursor is positioned on a star,
click
The plot above may have appeared differently if we
were plotting in units of
World Coordinates. if the image has a World
Coordinate System calibration, with Right Ascension and Declination
for every point, then you can choose to plot in those coordinates.
The choice is specified a number of places in Mira , one being in
the Image Context Menu > Plot menu. Right click on the
image to open the
Image Context Menu, select the Plot submenu,
then the check the World Coordinate
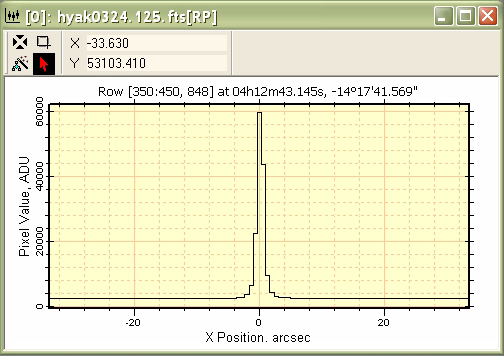
item. Then click To make the plot below, we used the image 'hyak0324.125.fts', which is a sample image having a World Coordinate System calibration pre-applied (note: the calibration is not correct but is included simply to show how World Coordinates are used).
The tutorial Tutorial: Displaying an Image Set shows how to Overplot the row profiles for members of an image set. Over-plotting Different Plot SeriesThe previous sections have described how to Overplot multiple line profiles by using Move mode for the Line Profile Plot. Mira also lets you Overplot the plot data (series) from any Plot window onto the data displayed in any other Plot window. To do this, use the Copy/Paste protocol to copy the series from a "source" plot and paste them into a "destination" plot. For example, using the image 'Hyak0324.120.fts' from above, let us compare a median combination of about 20 rows with a mean combination of the same rows. 1. Make sure the window containing the image is the window with focus (it shows the highlighted caption).
2.
Change the Image Cursor to a rectangle and
adjust the size to approximately 51 rows tall by 51 columns wide,
as shown below. The width may be any number, but this was the
default image cursor size when the window
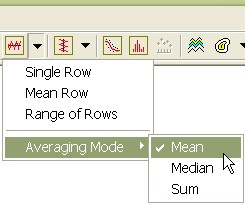
opened. In Image Cursor Mode ( 3. On the Image Plot Toolbar, click the down arrow next to the Row Profile command and select Averaging Mode > Mean as shown below.
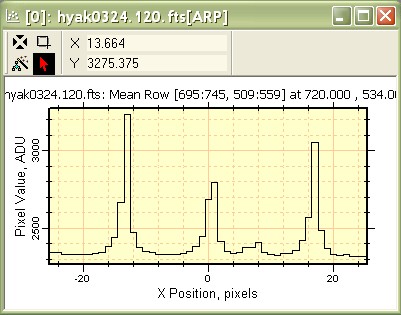
This creates a Mean row plot over 51 rows, as shown below.
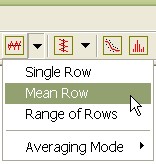
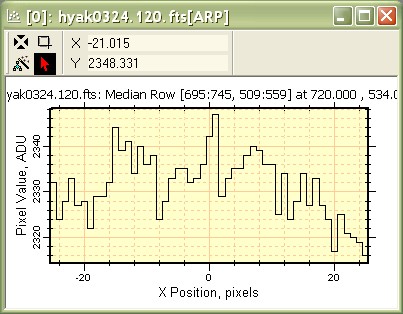
5. Repeat the previous step using Averaging Mode > Median followed by the Median Row command to create the following plot. If the toolbar command is not available, click on the image to give it focus and load its toolbar. Note that the Averaging mode change applies to this image window only. To make a setting the default, see Plot Averaging Mode
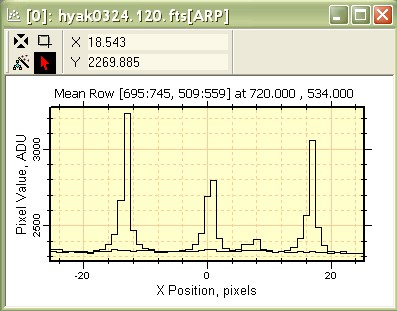
In the above plots, compare the Y AXIS scales to see the difference between the median of 51 rows and the mean of 51 rows. 6. Click the Median Row Plot (the first one of the two we created) to activate it. Now click the Edit > Copy command in the Plot menu or use Ctrl+C to copy the data from the Median Row Plot window. 7. Click the Mean Row Plot window to activate it. Now click the Edit > Paste command in the Plot menu or use Ctrl+V to paste the data into the Mean Row Plot window. The result looks like the following:
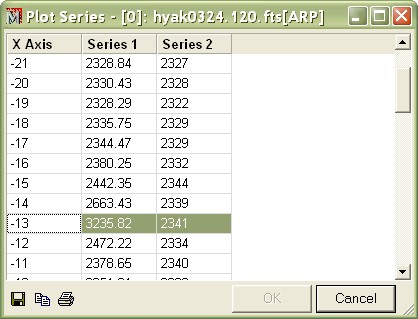
After you paste the data into the window as shown above, you might wish to open the Plot Animation Bar so you can blink between the plot series. You will also notice that the plot caption changes when you change the series. Accessing Plot DataYou can access the plot data values directly using the Plot Series Data command. With the last window active, right click on it to open the Plot Context menu, then select the Plot Series Data command. This opens a window which looks like the following:
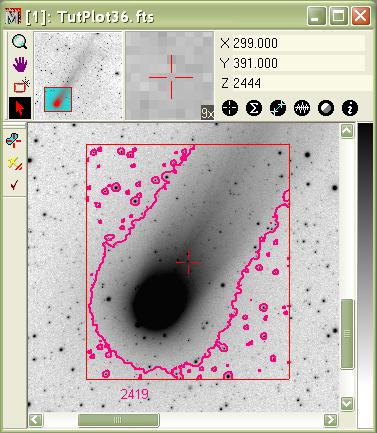
In the Plot Series dialog, the row at X Axis = -13 has been highlighted by dragging the mouse point across it to show a position where the mean and median row values are very different. You can also see this in the plot windows above. You can save the data from the Plot Series dialog using the buttons on its bottom border or by using commands in its context menu (right click on the table to open). See Plot Series Data. Creating a Contour PlotMira provides two ways to plot contours on an image: 1) Contours computed at specific intensity levels, and 2) a single contour computed at a level you mark on the image. Here, we will mark a contour on the comet image we have been using thus far. To interactively draw a contour, do the following:
In the picture below, the contour was marked at an intensity value of of 2419. One way to enhance the information give by the contour is to switch to a pseudocolor palette and adjust it to appear dark near the intensity level of the contour but to show color above and below that value.
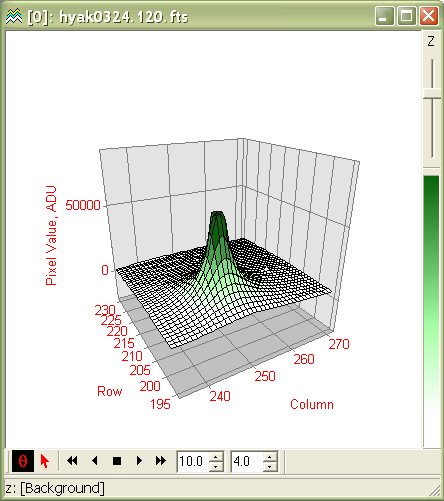
Creating a 3-D Surface PlotMira can quickly create a 3-D Surface Plot showing the surface intensity versus (column,row) position in the image. Like contour plots, 3-D plots work with the region bounded by the Image Cursor and should be constrained to a small number of pixels, usually not more than 10,000 pixels in area unless the image is very noise-free. Otherwise, plotting many pixels often just shows a rough noise surface with little information. Various types of 3-D plots are available; see 3-D Pixel Representations to view some of these variations. To create a 3-D plot for a region of the comet image,
Related TopicsTutorial: Displaying an Image Set
Mira Pro x64 User's Guide, Copyright Ⓒ 2023 Mirametrics, Inc. All
Rights Reserved. |
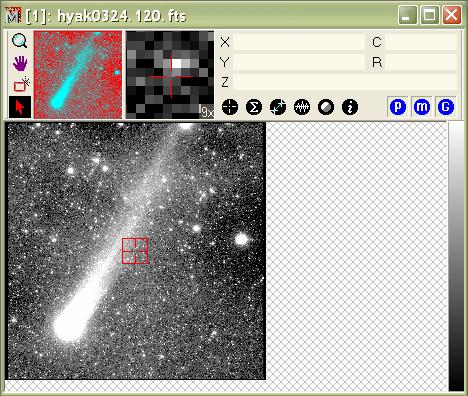
 Outline a region of interest
by positioning and sizing the
Outline a region of interest
by positioning and sizing the