|
Combine Image Set
The Combine Image Set command combines the
members of a displayed
Image Set into a single new image. Several
statistical methods are available for combining the images and for
adjusting ("normalizing") them to a common reference value (see
Statistical Estimators for Image
Combining).Normalization is used to adjust the images to a
common statistical value when using any combining method that
rejects bad data such as the mean, rank, and alpha methods.
Statistical methods for computing the normalization values are
discussed in
Region Statistics Estimators. This command is
often used following image registration. The related
Combine Files command works with images in files,
rather than displayed in memory.
|
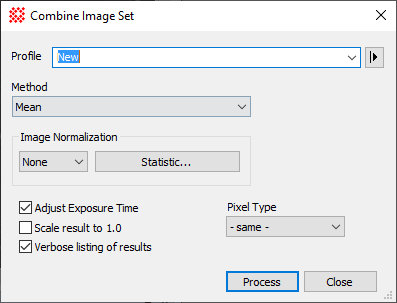
Combine Image Set Properties
|
|
Profile [|>]
|
Selects the parameter profile for this command and
allows you to save or work with existing presets.
|
|
Method
|
This list box selects the type of processing used
to combine the image values. These are described in
Statistical Estimators for Image Combining. If
the combining method has parameters, such as high and low sign
clipping limits, they are shown in fields to the right of the
Method selection.
|
|
Image Normalization
|
This control group specifies whether the images
are adjusted (normalized) to a common statistical value before
being combined. If normalization is not set to "none", then
the[Normalization Statistic] button
opens the
Region Statistics dialog. In this dialog you specify
how the normalization is to be computed, including the target
statistic and the region over which it is calculated. See the
discussion below.
|
|
[Normalization Statistic]
|
Click this button to open the
Region Statistics dialog for selecting normalization
properties.
|
|
Pixel Type
|
Select a Pixel Type for the output image that can
accommodate the increased signal and dynamic range of the combined
images. For example, if combining a large number of 16-bit integer
type images it is usually prudent to set the Pixel Type of the
output image to 32-bit real.
|
|
 Adjust Exposure time Adjust Exposure time
|
Check this box to update the exposure time in the
output image so that it is characteristic of the exposure time of
an equivalent single image. This can be used to maintain the image
flux, or the value of signal per unit time. This option also
updates the mid-time of the exposure based on the weighted
combination of the mid-times of all the combined images. The
mid-time is saved in the keywords
DATE-MID and TIME-MID, which can be used by the
photometry tools.
|
|
 Scale Result to 1.0 Scale Result to 1.0
|
Check this box to normalize the combined image to
a reference statistical value of 1.0. The Normalization settings are used to compute and
apply the scaling. Use this setting, for example, when creating a
flat field correction frame manually, rather than by using the
Create Master Flat command.
|
|
 Verbose listing of
results Verbose listing of
results
|
Check this box to list detailed messages about the
combining process.
|
Normalization
Normalization is used to adjust the images to a
common statistical value when using any combining method that
rejects bad data. This is essential when using a combining method
that performs rejection of bad data, such as the Sigma Clipping,
Min/Max or Median methods.
Choose the normalization operation, Scale, Offset,
or None, according to the nature of the difference between the
images being combined.
-
If the pixel values differ because of an
additive offset, like variations in the CCD bias offset, select
Offset.
-
If the images differ because of a scale factor,
as caused by differences in illumination or exposure time, select
Scale.
-
The None setting disables normalization.
This part of the combining procedure works like to
the
Normalize Image command.
Related Topics
Image Math Commands
Combine Files
Normalize Image
Image Set
Statistical Estimators for Image Combining
Region Statistics Estimators
Region Statistics
Image Registration
Profiles
Mira Pro x64 User's Guide, Copyright Ⓒ 2023 Mirametrics, Inc. All
Rights Reserved.
|