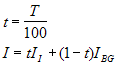|
|
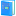
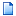
Imbed Image The Imbed Image command inserts an image into another image, treating the other image as a background. The background (background) image may be considered opaque, in which the imbedded image replaces all pixels underneath, or it may be assigned a transparency value to blend with the pixels of the imbedded image. The imbedding image is positioned over the background image using "corner offsets" in the column and row directions. The offset values are integral values and may be positive, negative, or 0. To imbed an image with a fractional pixel position, use the Shift Image command to perform the fractional pixel adjustment and then use the current command to complete the process using whole pixel offsets.
Imbed Image Properties
TransparencyThis method imbeds, or "pastes", a second image into another image which serves as the background, or "background" image. The imbedding can be either opaque or transparent. If no transparency value is specified, an opaque insertion is done—that is, the second image replaces the background image underneath it. The Transparency parameter specifies the percent transparent of the Background image. Transparency applies only over the region where the two images overlap. To describe transparent imbedding mathematically, consider imbedding image II into the current image IBG which acts as the background. Converting Transparency from percentage T to a decimal value t, we have the following equation for the intensity of the final image I:
For example, if Transparency = 25, then the current (background) image is only 25% transparent, and the resulting image contains 75% of the current image. By this definition, the opaque mode corresponds to a transparency of 100 percent, in which the current image is totally transparent and is replaced by the imbedding image. In general, the higher the transparency value, the greater the percentage that the imbedding image replaces the pixels of the background image. Insertion PointThe insertion point is determined by coordinate offsets in the background image where the origin (or "corner") of the imbedding image is to be placed. Since pixel coordinates are referenced to 1,1 at the image origin, the offsets to use are given by the following formula: Offset = Insertion Point - 1 where Insertion Point is a pixel coordinate in the Background image. Both column and row coordinates obey the same formula. For example, to imbed an image at background coordinate 400, 100, use Offset values 399, 99. Thus setting Offset values 0, 0 pastes the Imbedding image into the Background image with the two origins aligned at pixel coordinate 1, 1. Related Topics
Mira Pro x64 User's Guide, Copyright Ⓒ 2023 Mirametrics, Inc. All
Rights Reserved. |