|
|
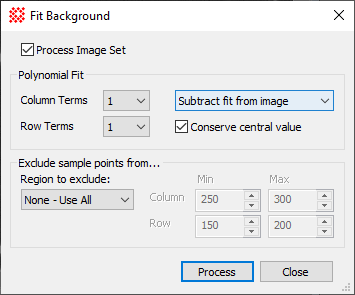
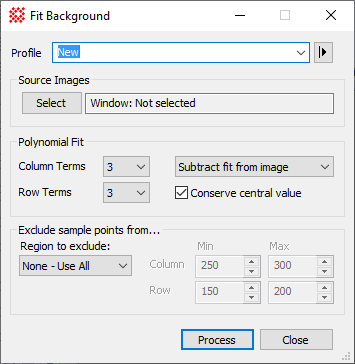
Fit Background The Fit Background command computes a polynomial fit to an image surface and applies the fit to the image. The fit may be subtracted from the image or divided into the image to flatten the image background. You also can choose to store the fit surface in the image data to save the surface as a separate image.
Correct Background Properties
Overview of Background FittingThis command calculates and (optionally) corrects either an additive effect, like scattered light, or a multiplicative effect, like vignetting, by fitting and applying a polynomial surface to the image. The polynomial ranges from 1x1 to 10x10 (100 terms). Clearly, 1x1 represents a constant value, but 1x2 and 2x1 represent a slope parallel to 1 axis. A 2x2 polynomial models a warped plane. A 3x3 fit involves a paraboloid and often is a good starting point for correcting calibrated images that appear to show poorly corrected vignetting which results from the optical axis shifting relative to the flat field images. In general you should use the lowest order that adequately flattens the background. The quality of the correction can be assessed by carefully examining the image at high contrast or after adjusting the palette, by making a contour plot, or by evaluating horizontal and vertical cross sectional plots at various places on the image (see the example, below). ExampleThe following example shows the power of this command by correcting an extreme example of background curvature. The "before" image below shows a flat field frame, which was selected because it had a large amount of background curvature:
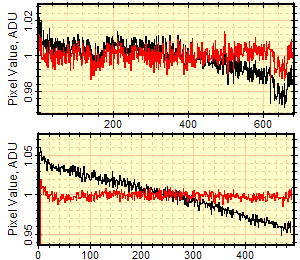
Below are shown cross sectional plots which illustrate the degree of non-flatness in the image. Black curves show the original image, red shows the corrected image. The small dips in the upper curves are caused by dust shadows on the flat field image and are not related to the background curvature. The data were over-plotted using the Plot Series Properties command and the Copy+Paste capability of Plot windows.
The "after" image below shows the result of correcting the background using the Conserve signal as image center option. In this view, the palette was stretched to high contrast for close evaluation of the image flatness. Notice that the deviations from flatness are now significantly below the noise level over all but the extreme edges of the image.
Related Topics
Mira Pro x64 User's Guide, Copyright Ⓒ 2023 Mirametrics, Inc. All
Rights Reserved. |