|
|
File Event Scripting File Event Scripting is a powerful tool used for running real time, script-driven processing of data files. The script executed upon detection of a file event may do anything a Mira script may do but, usually, the script processes the file that triggered the event. This feature monitors or "watches" a folder for a file event involving adding (saving), renaming, or deleting a file. For example, if a camera acquires an image, Mira could trigger on the file saving event, then run a calibration and measurement script on the image. Common applications for file event scripting include tasks like immediate processing or analysis of acquired images or other data files and synoptic astronomical work such as monitoring variable stars or detecting changes in point spread function or atmospheric transparency. File Event Scripting is controlled by a simple dialog where the monitoring strategy and scripts are specified. It is the scripts that do the work of processing the data in the file event. Once launched, the event processing runs in a separate thread of execution until stopped by the user. Using a separate thread allows Mira to be used for other activities while event monitoring and processing continues. See the tutorial Introduction to File Event Scripting for a guided example including sample scripts.
It is strongly advised that you complete the Tutorial to fully understand the use and potential power of File Event Scripting. Strategy behind File Event ScriptingFile Event Scripting is a process in which a Mira script is triggered and executes upon a file event. A file event is defined as a change in any file inside a continuously monitored ("watched") folder. The complete process goes as follows:
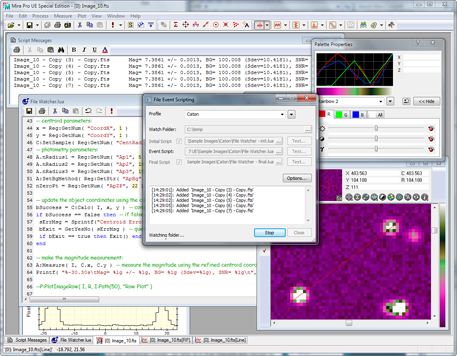
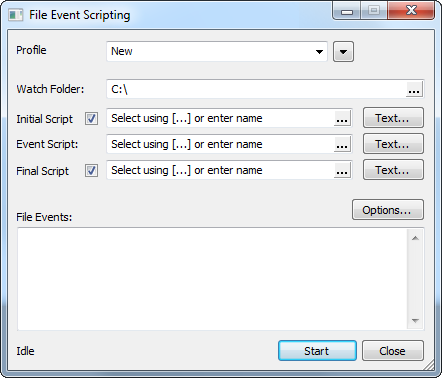
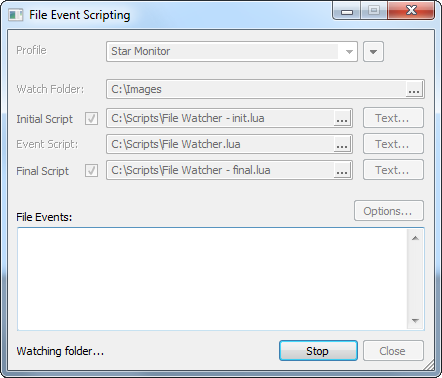
1. Set properties in the File Event Scripting dialog: Specify the Event Script file. Specify optional Initial Script andFinal Scripts. 2. Click the [Start] button to begin. The following steps occur: The optional Initial Script may be called once. Optional Text may also be passed to set script properties. 3. Folder monitoring continues to watch for file events. Each file event results in the following task: The Event Script is called to process the file. Optional Text may be passed to set script properties. The Event Script is called to process the file. Optional Text may be passed to set script properties. The Event Script is called to process the file. Optional Text may be passed to set script properties. ... until terminated by clicking the [Stop] button. 4. Stop event monitoring by clicking the [Stop] button. The optional Final Script is called. Optional Text may be passed to set script properties. 5. Event Scripting dialog returns to the idle state. All dialog controls are enabled. The File Event Scripting Control DialogThe File Event Scripting dialog is the master control center for event scripting. The dialog has different appearances depending on whether it is active or inactive, as shown in the 2 pictures below. The dialog can be resized to expand the text fields.
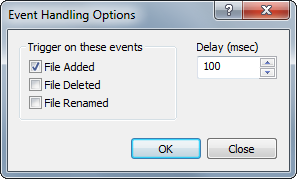
The Event Handling Options dialogClicking the Options button opens the Event Handling Dialog where you indicate the trigger for executing your event script:
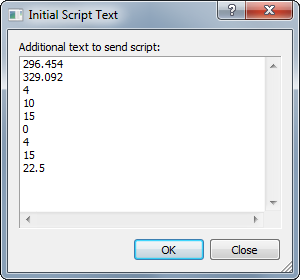
As mentioned above, there are 3 possible script types: Initial, Event, and Final. Each type of script may be sent properties in the form of text values (note that a script may also get parameters from the Windows Registry or a file). These properties are entered by clicking the [Text...] button next to the script type. It is the script's business to know how to use these values. For example, test parameters for initializing photometry are shown below for the Initial Script. These are the initial object coordinates in pixel units, radius values for three apertures, and other parameters.
Related TopicsTutorial: Introduction to File Event Scripting
Mira Pro x64 User's Guide, Copyright Ⓒ 2023 Mirametrics, Inc. All
Rights Reserved. |