|
|
The Aperture Photometry package is used to make photometric measurements of stars and other small objects using the aperture photometry method. This suite of commands is extremely versatile and can be used for measuring 1 or more objects, with 1 or more standard stars, in either a single image or multiple images in an Image Set. Applications include techniques such as differential photometry, time series photometry, and weighted ensemble photometry. The results can also be used for all-sky photometry, but Mira does not compute or apply the extinction corrections and color transformations (although these tasks can be programmed using the Pro Script module). This command uses the Aperture Photometry Toolbar (see below). This is a standard command toolbar interface to a suite of commands. Aperture photometry results are reported in a Grid Control in either a Report Window or the Apphot Pane.
Getting Started with Aperture Photometry
Common Photometry Tasks
Aperture Photometry ToolbarAperture photometry commands are operated from the
toolbar shown below. Some commands are also accessed from the
Properties
dialog, which is opened using the
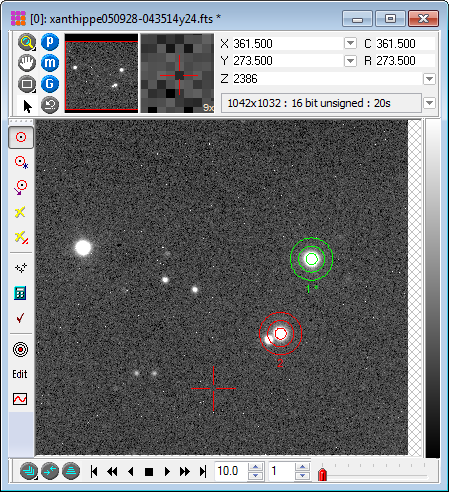
The The results of photometric measurements are listed in the Apphot Pane, a type of Measurement Pane. All reported quantities are defined in Photometric Measurement Definitions and Photometric Error Definitions. You can copy or save the results from this window, plot a light curve, or make a scatter plot of values in two table columns. For example you might plot the Error vs. Magnitude. If doing photometry of an Image Set, then you might plot Magnitude versus Julian Date. OverviewThe Image Window below shows an image with 2 marked objects, one a standard star and the other the target object to be measured. Each marker includes 3 apertures. The inner aperture measures the total signal from the object + sky, and 2 outer apertures define an annulus for measuring the local brightness of the sky background. The background is subtracted from the [object + sky] measurement to obtain the net signal attributable to the object. This is converted to a magnitude as described above and is listed in the Apphot Pane. The Aperture Photometry Toolbar is shown on the left window border.
Additional Features
Automated Processing of Multiple Objects in Multiple FramesMira provides a semi-automation capability for measuring objects in multiple frames using the importing facility. In this case, you import the coordinates of the objects from a text file "database" and have Mira process the objects in all images of an image set. Object data may be imported in (column, row) coordinates or, for FITS format images having a WCS ( World Coordinate System) calibration, in (RA, Dec) coordinates. See the Import Photometry Catalog command. Related TopicsAperture Photometry Properties Tutorial: Introduction to Aperture Photometry Tutorial: Doing Time Series Photometry Using Edit Mode in Aperture Photometry
Mira Pro x64 User's Guide, Copyright Ⓒ 2023 Mirametrics, Inc. All
Rights Reserved. |