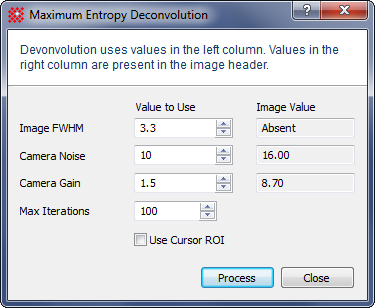
Maximum Entropy Deconvolution
The Maximum Entropy Deconvolution method sharpens an image while reducing noise. Maximum entropy processing works best on images having high contrast and high signal to noise ratio. See this Example. The High Pass Filter is quicker but does not reduce the noise as does maximum entropy processing.
This command opens from the Process > Filters menu.

Properties of Maximum Entropy Deconvolution
|
Initial FWHM |
The Full Width at Half Maximum (FWHM) of the point spread function for the image, measured in pixels. This measures the amount of smearing in the image. It is important not to overestimate this value or this could lead to rings around point sources and edge ripples. The value should not be less than about 2.0. |
|
Camera Noise |
For a CCD camera, this is the Readout Noise. This quantity is measured in electrons (e). For example, if the readout noise is 9.2e-, enter 9.2. |
|
Camera Gain |
The ratio of output signal number to input electrons. This is a value like "2.8", meaning 2.8 electrons per Digital Number ("DN", also called "Count" or "ADU"). Electronically, this is actually the "inverse gain" but is referred to as the gain for a CCD camera. |
|
Max Iterations |
Specifies the maximum number of iterations of the deconvolution. Mira will stop early if no change is detected. |
|
Use Cursor ROI |
If checked, only the region inside the cursor is deconvolved. Otherwise, the entire image is processed. |
Maximum Entropy only works with luminance images. It does not work with RGB images. If you want to process an RGB image, you will need to extract the channels and process them separately. However, the dynamic range will be lower since each channel of the RGB image will have been reduced to 256 levels. For RGB images, it is best to perform Maximum Entropy processing on the luminance images before merging then into RGB form.
|
Tip |
When MaxEnt processing is active, you can break out of the loop at any time using the [Esc] key. |
For best results, the Properties must be chosen carefully. Mira's implementation of Maximum Entropy processing uses 3 Properties: FWHM, Camera Noise, and Camera Gain. The dialog shows two sets of Properties:
The left column lists values that will be used.
The right column lists values taken found in the image header.
Values in the right column are shown simply as a guide in choosing the Properties that are used from the left column.
The number of Iterations defines how many cycles to refine the deconvolution result. More cycles are not necessarily better. Using too few iterations does not give MaxEnt a chance to converge to a good solution, whereas giving too many cycles can go beyond the optimum result and lead to an overly processed appearance full of artificial rings, dimples, and ripples. The number of iterations will change with images of different properties and according to the other Properties used. An iteration count in the range 20 to 100 is typical.
The ROI, or Region of Interest, is the enclosing rectangle where MaxEnt will be applied. This rectangle is defined by the Image Cursor. Choose the ROI so that it encloses only the region that needs to be enhanced. Enhancing the background may be of little value so it is not worth waiting on the extra computing time.
Spatial Filter Commands, Example of Maximum Entropy Processing, High Pass Filter