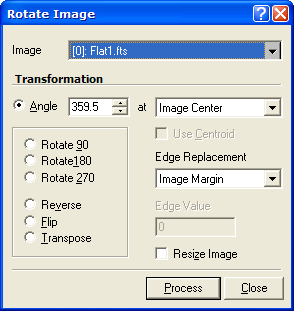
Rotate Image
The Rotate Image command can rotate an image or image set in 90 degree steps, perform mirror flips, transpose about the main diagonal, and apply free rotation to any precision angle. If you want to apply scaling or shifting operations to the rotated image, it is best to perform the operations together, in one mathematical step, using the Affine Transformation command.
This command opens from the Process > Geometry menu.

|
Angle |
The rotation angle, measured in degrees. |
|
at |
The center of rotation, either the center of the image or near the center of the image cursor (see section below) |
|
Use Centroid |
If selecting the Image Cursor option, check this box to have the center of rotation at a centroid position near the center of the cursor. For example, you may want the image rotated about the center of a star. |
|
Resize Image |
Check this box to allow the image to be enlarged to hold all pixels after rotation. If this box is not checked, the image size remains the same and the corner pixels rotate outside the visible image. |
|
Edge Replacement |
Defiens the method used to evaluate "blank" pixels when the rotation brings non-existing data into the output image. |
|
Edge Value |
Defines the method used to assign values to the edge pixels. The options Value and Image Margin are described in the section below. |
|
Rotate 90 |
Rotates 90 degrees in the positive sense. |
|
Rotate 180 |
Rotates 180 degrees. |
|
Rotate 270 |
Rotates 270 degrees in the positive sense. |
|
Reverse |
Mirror flips the image in a left/right sense. |
|
Flip |
Mirror flips the image in an up/down sense. |
|
Transpose |
Flips the image about its main diagonal extending from pixel 1,1 to the opposite corner. |
The center of rotation can be selected 3 ways: The center of the image, the center of the Image Cursor, or the centroid point near the center of the image cursor. If using the image cursor be sure to position it before clicking [Process].
The "edge" refers to the blank pixels that rotate into the output image from off the edge of the original image. These pixels have no value but some values must be assigned to them in the rotated image. Examples
Mira gives you two options for assigning a value to the edge pixels:
Image Margin: Mira computes a value typical of pixels around the margin of the image.
Value: Mira uses the pixel value you specify in the Edge Value field. This can be a luminance value or a color value. For example, 0 and 500.25 are luminance values, and 255,128,0 is a color value.
The Transpose operation reflects pixels across the main diagonal of the image matrix. FITS image have their main diagonal running from the lower left toward the upper right. Other graphics formats have their main diagonal running from upper left to lower right.
Geometry Commands, Register Images