Calculate Gain
The Calculate Gain command measures the signal conversion of the camera electronics in terms of the light signal incident on the detector versus the pixel value in the digital image. The gain is expressed in terms of electrons per Analog to Digital Unit (ADU) or Digital Number (DN), as "e-/ADU". To make this measurement requires 2 bias frames and 2 flat field frames. Best results are obtained if the bias frames are taken sequentially and the flat frames are taken sequentially and exposed to the same illumination. As a by-product of the gain calculation, this command also reports the readout noise (or fundamentally base level of noise) produced by the camera.
This command is executed using the Diagnostics > Calculate Gain command.

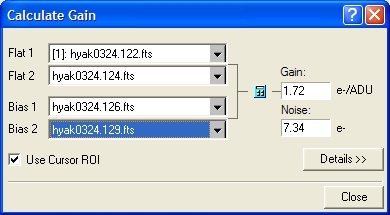
To make the measurement requires opening (displaying) 2 bias frames and 2 flat frames. These may be opened in separate window or as (part of) an image set. The images are selected using the 4 image list boxes shown in the dialog above.
Open 2 biases and 2 flat field frames.
Click the Measure > Diagnostics > Calculate Gain command to open the Calculate Gain dialog.
Using the 4 Image Tree controls, select the 2 bias frame and 2 flat field frames from among the open images.
Using the Use Cursor ROI option, choose whether to use the entire image for making the measurement or to limit the measurement to a region of "good" pixels. This is a statistical measurement and you do not want blank pixels or image defects affecting the statistics. Irregularities in the flat field structure, such as dust "donut" shadows do not affect the measurement.
Click ![]() .
.
To view details of the measurements and the calculation, click [Details >>].